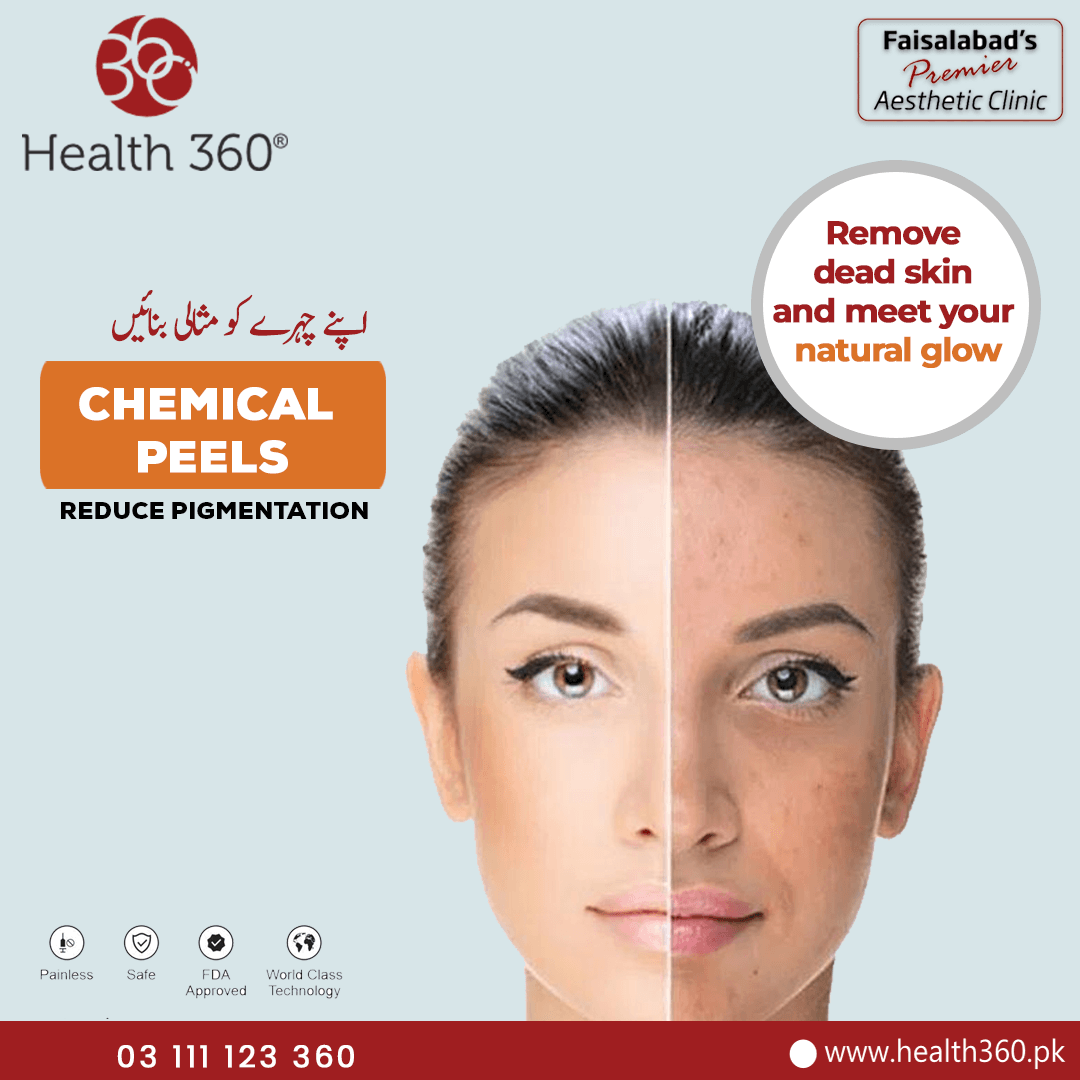
Chemical peels are dermatological treatments designed to exfoliate the outer layers of the skin, revealing a fresher, more vibrant complexion. They come in three main types: superficial, medium, and deep peels, each varying in strength and penetration levels. Superficial peels gently exfoliate the outermost skin layer, medium peels target the middle dermal layer, and deep peels penetrate several skin layers for more dramatic results. These treatments work by applying a solution that causes controlled tissue damage, prompting the skin to regenerate and heal.
Benefits of Chemical Peels
Chemical peels offer numerous benefits, significantly improving skin texture by promoting cell turnover and removing dead skin cells. This leads to smoother and softer skin. They also effectively reduce fine lines and wrinkles by stimulating collagen production, which tightens the skin. Additionally, chemical peels are highly effective in treating acne scars and hyperpigmentation by breaking down melanin clusters and encouraging new skin growth, which helps in evening out the skin tone.
Preparing for a Chemical Peel
Proper preparation is crucial to achieving the best results with minimal risks. Choosing the correct type of peel for your skin type and concerns is essential and typically involves consultation with a dermatologist. Pre-treatment skin care may include using prescribed products that prep the skin, like retinoids or glycolic acids. It is vital to avoid sun exposure and refrain from using harsh skin treatments like waxing or aggressive exfoliants prior to the procedure to minimize adverse reactions.
The Chemical Peel Procedure
The procedure generally begins with a thorough cleansing of the skin to remove oils and impurities. The chosen chemical solution is then applied to the skin, which may cause a tingling or burning sensation as it works to exfoliate the skin layers. The duration of the procedure varies; superficial peels might take just a few minutes, while deeper peels could last up to an hour. After the desired depth is achieved, the chemical solution is neutralized or washed off, concluding the treatment.
Post-Peel Care
Following a chemical peel, immediate aftercare is critical to ensure proper healing and maximize results. Patients are generally advised to keep the skin moisturized and protected from the sun using high-SPF sunscreen. Common side effects include redness, swelling, and peeling, which can be managed with recommended topical treatments and avoiding strenuous activities. Long-term maintenance involves a consistent skincare routine that includes gentle cleansing and periodic follow-up treatments as advised by the dermatologist.
Risks and Considerations
While chemical peels are generally safe, they do carry potential side effects like prolonged redness, scarring, or infection. Individuals with certain skin conditions or sensitivities may not be ideal candidates for chemical peels. Pregnant or breastfeeding women should avoid this treatment. A thorough consultation with a dermatologist is essential to evaluate the suitability of a chemical peel, discuss expectations, and outline a personalized treatment plan to minimize risks.
Comparing Chemical Peels with Other Treatments
Chemical peels differ from microdermabrasion, which mechanically exfoliates the skin’s surface without using chemicals. While both treatments improve skin texture, chemical peels tend to offer more profound and longer-lasting results. Compared to laser resurfacing, which uses targeted light energy, chemical peels can be less expensive and have shorter recovery times, depending on the peel’s depth. Overall, chemical peels stand out for their ability to deeply rejuvenate the skin, address a variety of concerns, and provide significant improvements with minimal downtime.